Osteoarthritis is a group of diseases that occur for a variety of reasons but are similar in terms of clinical manifestations and course. At the heart of all arthrosis is the defeat of the components of the joint. Osteoarthritis is a progressive disease with impaired function of the affected joint. Arthrosis (gonarthrosis) of the knee joint is a disease in which the cartilage, the joint membrane, the ligaments, and the periarticular muscles of the knee joint are damaged. Arthrosis of the knee joint, the treatment of which requires an integrated approach, also requires attention. And at least an elementary understanding of why and how the disease progresses.
Gonarthrosis: Causes
Causes of knee arthrosis may include:
- Joint Injuries: According to the scientific literature, about one-third, possibly half, of arthrosis is preceded by trauma. Someone may accidentally trip over the street or damage the joint while exercising. Acute pain occurs first, which later becomes dull and mild, but does not cause much discomfort. In most cases, the joint will soon heal and show no signs of injury. But in rare cases, this unfavorable coincidence of conditions can trigger the development of arthrosis.
- Long-term joint overload: It is believed that people whose vocation involves long-term excessive stress in the joints (professional athletes, postmen) may face the development of early joint arthrosis.
- Arthritis (inflammation of the knee joint): with inflammation of the joint, biological and morphological changes occur, blood flow is disrupted, so it is arthritis that causes arthrosis of the knee joints (secondary arthrosis).
Additional risk factors
- Heredity. Usually, arthrosis of the joints is not directly inherited, but the "catalysts" for the development of arthrosis may be the peculiarities of metabolism, the structure of cartilage tissue, which are only genetically propagated. The possibility of arthrosis can also occur if a person has joint disorders or immaturity, birth trauma.
- Overweight. Being overweight is an "aggravating" condition in the development of arthrosis: that is, it is not directly related, but weight gain is a big burden. It should be recalled that osteoarthritis of the knee is more severe in obese people than in others.
- Chronic stress. It is a well-known fact that in case of excessive experience, the adrenal glands release "stress hormones", which leads to a deterioration of the blood supply and a decrease in the production of hyaluronic acid, which is an important component of the normal functioning of the joint. Chronic stress and the above aggravating conditions can lead to osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of gonarthrosis
- Pain. One of the initial and main symptoms of knee arthrosis is knee pain. It is noteworthy that knee pain only occurs during physical exertion: when walking, running, squatting, and lying down, this pain goes away and disappears completely after a while (until the next load).
- Crack in the joint. In contrast to the "cracking" of the joints in healthy people, the cracking of the joints affected by arthrosis has a different tone: rough and "dry. "
- Joint stiffness. Grade 1 knee arthrosis is usually not expressed as rigidly as in the following stages. But as progression progresses, the range of motion of the affected joint decreases significantly.
- Deformity of the knee joint. As gonarthrosis progresses, abnormal formations develop in the spinal cord spine. Because of them, the joint may be different from a healthy look. In addition, the appearance of the joint may be slightly "bulky" due to excessive accumulation of intraarticular fluid (synovitis).
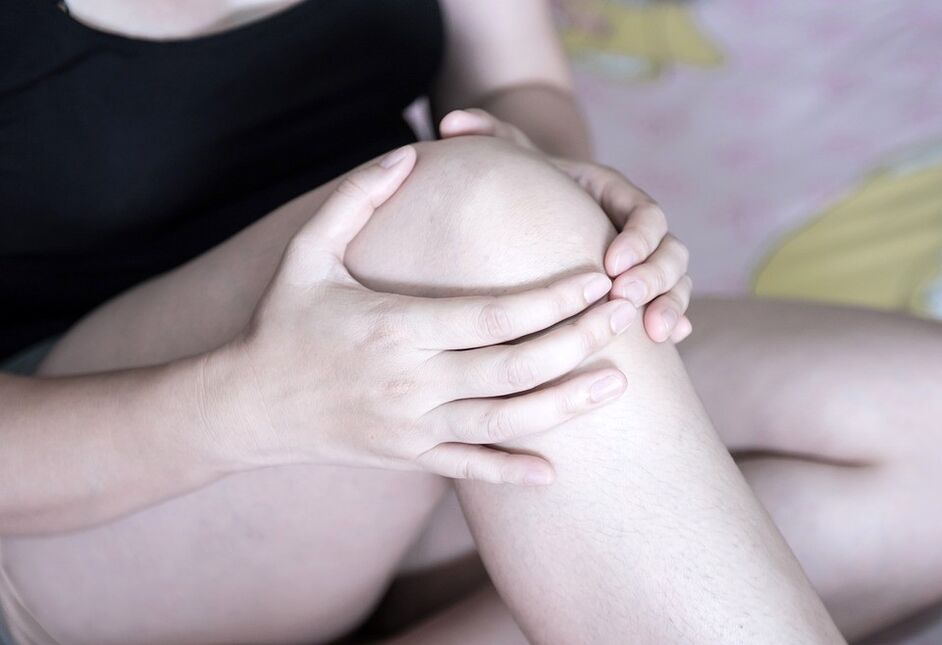

The course of arthrosis of the knee joint
Knee osteoarthritis most often affects women than men. This disease often progresses after forty, but sometimes occurs earlier, usually after injuries and in professional athletes. More complicated and severe gonarthrosis occurs than previously described in obese women and severe varicose veins.
The development of the disease is characterized by the appearance of minor knee pain. Often pain occurs when a person has to stand on his feet for a long time as he goes down and up the stairs. When a person goes to bed, the pain disappears, but when he has to get up, the first steps will be very painful for him.
The knee joint has three degrees of arthrosis
Arthrosis of the knee joint is 1 degree
Grade 1 knee arthritis is sometimes characterized by intense pain in the knee, however, the bones that make up the knee joint remain undeformed, but the knee may swell slightly due to synovitis. If there is too much intraarticular fluid, it can spread to the popliteal fossa. This condition is called Baker's cyst. If you have been diagnosed with such a diagnosis, you don’t have to worry, it’s not an oncological neoplasm, but is reduced by medications prescribed by your doctor.
Grade 2 knee arthritis
Grade 2 knee arthrosis begins 2-3 months after the onset of the disease. During this time, knee pain is usually worse. This pain no longer simply occurs during physical exertion, but accompanies the person with any movement. Usually at this time, a peculiar crack in the knee "joins" the pain in the joint. Grade 2 gonarthrosis of the knee joint is accompanied by a decrease in the ability to bend the foot in the knee joint in addition to intense pain and cracking. The deformation of the joint is immediately apparent: the bone structures change their shape, and when touched, the joint becomes hard and "rough".
Knee arthrosis grade 3
Grade 3 knee arthrosis is characterized by constant intense pain, and it is difficult for a person to be in a supine position: he is forced to look for a position in which to rest. The knees become sensitive to changes in the weather, and painful pains begin at night. Grade 3 gonarthrosis of the knee joint is associated with a permanent decrease in mobility, making it impossible for a person to bend their leg by more than 90 ° at the knee joint. Sometimes in grade 3 gonarthrosis it is not possible to straighten the leg completely, a person has to walk on slightly bent legs. In some cases, the deformation of the legs takes the form of an O or X shape. In extreme cases, a high degree of treatable arthrosis is required.
Knee gonarthrosis: treatment. What you need to know about medication for the knee
Although plenty of advertising promises wonderful ointments for joint pain, you need to understand that gonarthrosis cannot be cured by any method, an integrated approach is needed.
If you find the first signs of arthrosis in yourself, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. This could be an arthologist, rheumatologist, orthopedist or first time a GP.
Knee arthrosis: NSAID treatment
So how to treat knee arthrosis? Non-steroidal (non-hormonal) substances that can alleviate the inflammation of the joint are usually used to treat the joints. Gonarthrosis of the knee is treated with drugs that can have an antipyretic, analgesic effect. Remember that medicines in this group should not be taken continuously. they are able to "mask" the symptoms of the disease. Please note: do not self-medicate, only under the guidance of a qualified professional who can prescribe treatment for you, based on the individual parameters of your body, taking into account the contraindications to the use of medications.
In recent years, a new generation of drugs has been used in practice: selective agents that act in the same way as NSAIDs, but are less likely to cause unpleasant side effects and do not cause complications.
Knee arthrosis: treatment with chondroprotectors
With arthrosis of the knee joint, you can take substances that nourish the cartilage tissue in the joint and restore its structure. These drugs are chondroprotectors. Such drugs are most effective if you have grade 1 gonarthrosis of the knee joint, as there is almost nothing to recover from extreme gonarthrosis: virtually all cartilage is destroyed. To achieve the effect of chondroprotectors, they must be used for a long time: at least 2-3 courses of treatment, which usually takes a year and a half. Keep in mind that although there are few contraindications to this class of drugs, their use should be discussed with your doctor.
Knee arthrosis: treatment with vasodilators
Vasodilator drugs are a good complex therapy in the treatment of arthrosis. They help to restore the joint by improving blood flow and relieving spasms of small blood vessels. A pleasant bonus in treating knee arthrosis, including vasodilators, can be the elimination of nocturnal pain in the injured joint. If you want to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, vasodilators are best used with chondroprotectors, so that the nutrients in the chondroprotectors penetrate the joint in larger amounts and circulate more actively in it. Remember to talk to your doctor about taking this medicine.
Knee inflammation: medicinal ointments and creams
Healing ointments for arthrosis are used as a trap by marketers for desperate patients. Keep in mind that treatment with an osteoarthritis ointment for the knee joint will not yield extreme results, but in the initial stages, the cream and ointment can significantly alleviate the condition. Analgesic ointments can be used to improve joint circulation. Such drugs help to eliminate painful cramps in the joint, increase blood circulation. You can also use bee and snake venom-based ointments. These ointments have an irritating effect that increases blood circulation to the damaged joint. Keep in mind that many toxin-based ointments can cause allergic reactions, so only a professional should give permission to use them.
Therapeutic exercises for knee arthrosis
Therapeutic physical culture of knee arthrosis is an effective treatment method combined with medication and physiotherapy.
Remember that gonarthrosis healing gymnastics is the main method of treatment because we cannot strengthen the muscles and blood vessels in the knee joint and we cannot activate the blood supply with any medication. In addition, physiotherapy is the most costly and effective treatment that does not require unnecessary financial outlay.
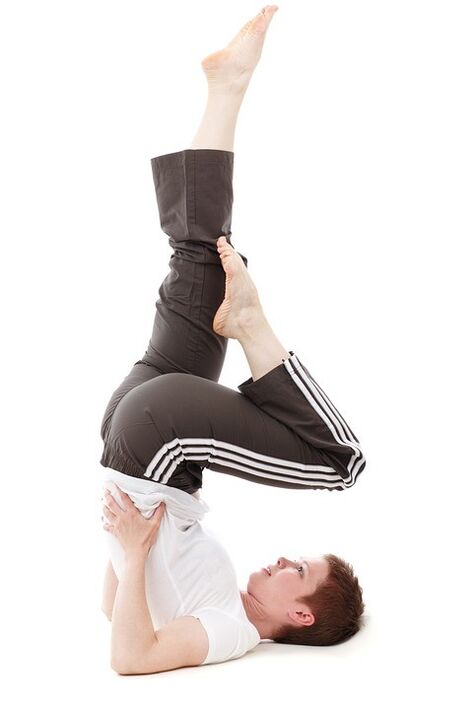

But the training complexes of arthrosis need to be done intentionally: don’t rush 200 squats or 100 kicks a day. Under no circumstances should you apply intense dynamic loads and perform static exercises instead of active flexing. Unfortunately, most patients don’t just like to do static exercises because they are most energy consuming and tiring, but if you persevere for 2-3 weeks, exercising regularly will not only improve the condition of the knee joint but also find an increase in strength and performance.
How to do it right
The exercises should be performed very smoothly and gently, applying light pressure to the ligaments and joints. Do not let intense pain during exercise. Aim for grade and regularity, don’t rush things: the expected effect can only be achieved with constant moderate effort.
Remember that strength exercises should not be applied for the first time after surgeries on the abdominal and chest organs, with fever, the critical days of women. It is absolutely necessary to pay attention not only to the joints, but also to the abdominal press and back muscles. This is necessary so that the main blood flow to the limbs passes through the muscles of the abdomen and back.
The training complexes are freely available on the internet, try to do different exercises for 30-40 minutes a day, following the instructions.
We wish you perseverance and will to move easily!
Physiotherapy for arthrosis of the knee joint
If you ask if it is possible to use physiotherapy methods in knee arthrosis, we will answer - definitely!
Knee arthrosis: treatment - laser therapy
Laser therapy is the use of a beam of light for therapeutic purposes consisting of ultraviolet, infrared, red radiation spectra. The laser has anti-inflammatory, decongestant and analgesic effects. Typically, the process of laser therapy consists of 15 sessions. Laser therapy is a relatively safe method of treatment, but it is impossible to cure arthrosis with a single laser, it is an additional method of treatment.
Knee arthrosis: treatment - cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is the effect of local cooling on the joint. There are two methods of cryotherapy: applying a cryosauna and applying liquid nitrogen directly to the joint. The latter method is thought to be the most effective in knee arthrosis. Cryotherapy can help improve the blood supply to the joint, improve metabolic processes and relieve muscle cramps. The course of treatment is usually 10-12 times a day.
Knee arthrosis: treatment - magnetotherapy
Magnetotherapy - exposure to a magnetic field. Physiotherapy is a fairly common method in hospitals and clinics. Exposure to a magnetic field has anti-edematous, non-contact electrical muscle stimulation and reduces joint inflammation. The cure is prescribed by a doctor - physiotherapist.
Knee arthrosis: treatment - ultrasound therapy
Ultrasound therapy - treatment with sound waves. Ultrasound of arthrosis improves blood supply, reduces muscle cramps, and has an analgesic effect. To enhance the therapeutic effect of ultrasound, a drug is applied to the affected joint. Ultrasound waves make it easier for the drug to penetrate the tissues.
Knee arthrosis: heat treatment
Heat treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee is used in stages 1-2 of the disease. This method includes the treatment of ozokerite, paraffin, sludge. The latter deserve special attention: sludge treatment for arthrosis can also be done at home. It is necessary to dilute the medicinal sludge with water and heat it to 60 ° C, then mix the resulting mass with unheated sludge, cool to 38-42 ° and apply a 2-3 cm thick layer to the affected joint. Cover the mixture with oil cloth and a warm blanket. Leave on for 30 minutes. Perform the procedure every other day with a course of 10-12 procedures.
Diet and herbal medicine for knee arthrosis
Diet for arthrosis is an important factor in successful treatment. But we need to understand that the development of osteoarthritis is not related to any specificity of nutrition, but obesity contributes to the incidence of osteoarthritis of the lower extremities. Still, you need to lose weight correctly: by no means can you starve or sit on hard diets, because as you know, after leaving hard diets, you gain weight again, and often in even larger amounts.

We need to know that being overweight is also a disease, but it can and should be treated. In the case of obesity, the regulation of the centers of appetite and satiety is confused, but it is possible to "steer them" in the right direction.
First, you need to recognize that there is a problem that is often associated with poor eating habits. Second, you need to learn to set realistic goals for yourself. A 10-15% weight loss from baseline is an excellent result. Believe me, even if you lose even 5% of the original, you will feel immediate relief: your blood pressure will drop and your joints will improve.
The goal is to lose weight
In any case, if you have set yourself the goal of losing weight, you need to rethink your diet, composition, and the amount of food you eat. Reduce your consumption of confectionery, baked goods and all sorts of "fast" carbs.
For starters, we recommend that you try a simple diet. Prepare your usual diet by placing the regular dose on a plate. Now eat only half of the food on the plate. You will soon notice that you only eat the whole portion out of habit, although you need very little to satisfy your hunger. Even if you are hungry, slowly consume half the dose and rest for 10 minutes. You’ll be surprised that after this time, you just don’t want to finish the remaining dose: the hunger is gone, and with it the frantic desire to eat everything. After two months of such "malnutrition", you will achieve a noticeable result. Try!
In addition to proper food intake, do not forget about adequate fluid intake. People who do not have severe cardiovascular or kidney disease, as well as those who do not suffer from edema, can safely increase the amount of fluid they consume to up to 2 liters a day.
Alternative treatment of knee arthrosis
Herbal medicine for arthrosis. It is important to note that infusions and decoctions of arthrosis are weaker than the above methods, but may be relatively advantageous.

You can use one of the following infusions during the month:
remember that you must take each infusion or decoction separately and then replace it with another. Do not drink at the same time!
Birch decoction in case of arthrosis
Birch decoction for arthrosis: Pour 1 tablespoon of birch buds into a glass of boiling water, simmer the mixture for 15 minutes, and let it cook for 1 hour, warmly covering the container. After one hour, filter and add the broth with boiled water to the original volume. Take a quarter (1/4) cup infusion 4 times a day, one hour after a meal for a month.
Linden infusion for osteoarthritis
Linden infusion for osteoarthritis: 3 tablespoons of linden flowers should be poured with a glass of boiling water, simmer for 15 minutes, then cooled and filtered. Take a warm infusion 3 times a day with 1 glass after a meal for 3 weeks.
Burdock decoction for arthrosis
Burdock decoction for arthrosis: 1 tablespoon burdock root should be poured 1 cup boiling water, approx. Simmer for 30 minutes, stirring often, then cool the broth at room temperature and filter. Take the broth three times a day in a half (1/2) cup before eating for a month.
Alder infusion for osteoarthritis
Alder infusion for osteoarthritis: 2 tablespoons gray alder cone (Alnus incana) should be poured with 1 glass of boiling water, kept at low temperature for 15 minutes, then cooled and filtered. Take a third (1/3) cup of alder cone infusion 3 times a day for half an hour before meals for a month.
Collection of herbs for arthrosis
Collecting herbs for arthrosis: mix willow bark, parsley root, black elderflower and nettle leaves in equal parts, chop thoroughly. Pour 4 tablespoons of the mixture with 1 liter of boiling water and boil on low heat for 5-10 minutes, then leave for 2 hours and drain. Take this collection in a half glass 4 times a day for half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that arthrosis is a very unpleasant disease, faced with the need to draw the right conclusions from the disease, reduce negative emotions, start fighting for your full physical and mental health, taking into account the suggestions we have proposed. Then you will surely defeat the disease!